In a surprising twist in the evolving narrative of U.S. labor movements, workers at the Mercedes-Benz plant in Vance, Alabama, have decided against joining the United Auto Workers (UAW) union. This decision comes closely on the heels of a significant union victory at a Volkswagen (VW) plant in Tennessee, highlighting a divergent path in the southern U.S. automotive sector’s approach to unionization.
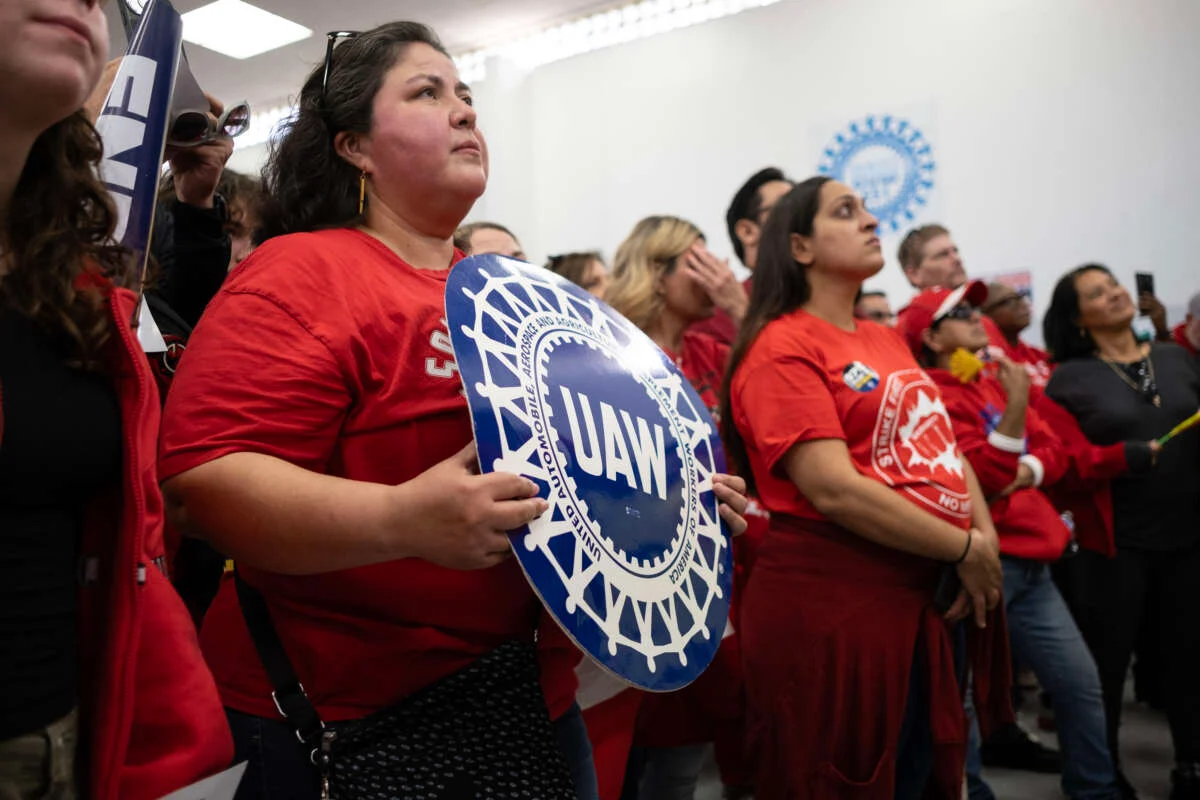

The Context of the Vote
The Mercedes plant, responsible for manufacturing the electric EQS and EQE SUVs among other vehicles, witnessed a closely watched vote. Despite the union-friendly climate following the VW victory, Mercedes workers cast their ballots with a definitive 56% majority opposing UAW membership. This result has halted, at least temporarily, the UAW’s momentum in a region traditionally resistant to unionization.
The Broader Implications of the Vote
This decision not only impacts the approximately 5,200 workers at the Alabama facility but also resonates through the auto industry and labor movements across the nation. The rejection at Mercedes contrasts sharply with the recent successful unionization at the New Flyer bus plant in Alabama, which notably also manufactures electric vehicles. This juxtaposition raises questions about the factors influencing union acceptance in different workplaces within the same industry and region.
Analyzing the Resistance to Unionization
Several dynamics played into the Mercedes workers’ decision. Reports indicate that the plant’s management may have conducted anti-union campaigns, including the showing of anti-union videos and the employment of firms specializing in dissuading union efforts. Such tactics, alongside a political climate in the South that generally favors lower unionization, might have swayed the vote. Additionally, the economic environment—with Mercedes and other automakers recently raising wages—may have lessened the immediate appeal of union promises.

The Legal and Political Landscape
The vote at Mercedes comes amid a broader discussion about workers’ rights and unionization across the U.S. Southern states, including Alabama, often have “right-to-work” laws and traditionally exhibit lower unionization rates. Moreover, political leaders in these states have actively discouraged unionization efforts, with Alabama Governor Kay Ivey recently signing legislation that penalizes companies recognizing unions voluntarily.
The NLRB’s Role and Ongoing Investigations
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) is actively involved in investigating allegations of unfair labor practices not only against Mercedes but also Hyundai and other firms in Alabama. These investigations could potentially impact future unionization efforts and labor practices at these plants.
Future of Unionization in the U.S. Auto Industry
Despite the setback at Mercedes, the UAW remains optimistic about the future of unionization in the U.S. auto industry. UAW President Shawn Fain has termed the push for union membership across U.S. automakers as the “UAW bump,” suggesting that union efforts lead to broader industry improvements in wages and working conditions. The UAW’s strategy moving forward will likely involve continued attempts to unionize other plants, including those owned by foreign automakers in the South.
The Global Context and the German Model
Internationally, the contrast is stark, particularly with Germany, where labor representation on company boards is mandatory for larger firms, and the auto industry is almost universally unionized. This global perspective may influence future discussions and policies regarding labor practices in U.S. subsidiaries of foreign companies.
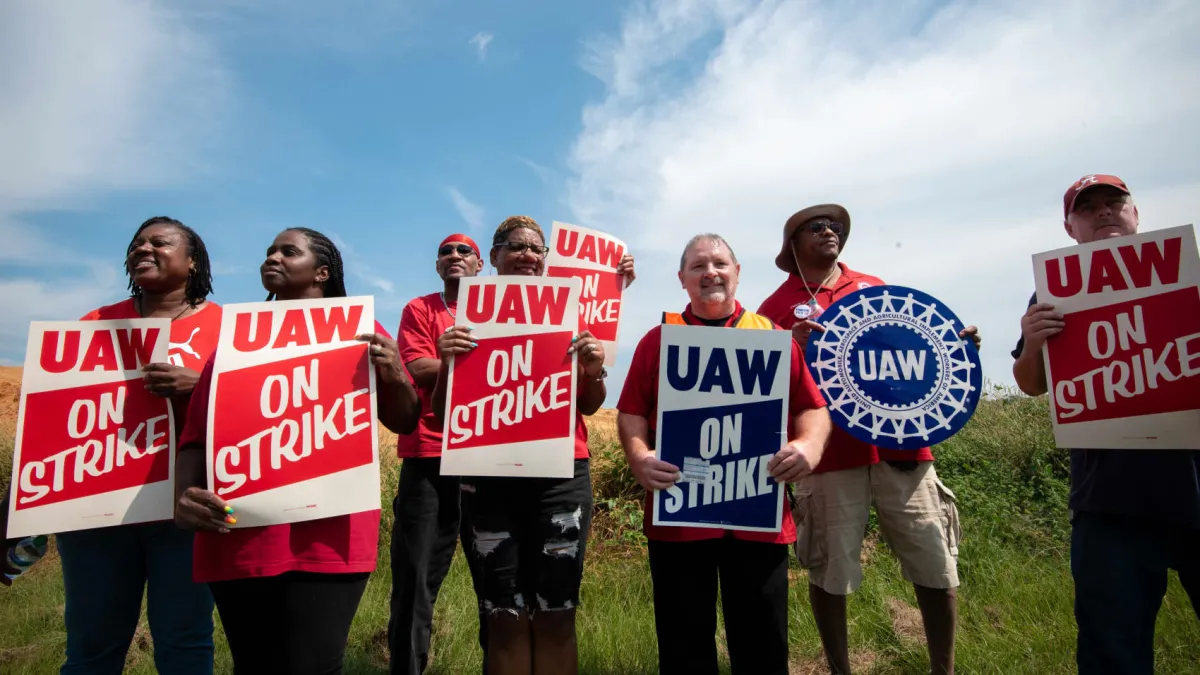

UAW Rejection at Alabama Mercedes: Labor Dynamics
The rejection of the UAW at Mercedes in Alabama illustrates the complex tapestry of labor relations in modern America, where economic, legal, and cultural forces intersect to shape the landscape of workers’ rights. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, particularly with the shift towards electric vehicles, the role of unions and the nature of labor relations will remain pivotal topics of discussion and action.