Smart devices have become an integral part of our daily lives, connecting us to everything from home automation systems to global communication networks. While these devices bring convenience, they also present security risks, as they are potential targets for hackers and data breaches. Keeping your smart devices secure is essential to protecting your personal information, privacy, and overall safety.
This article presents 90+ tips to keep your smart devices secure, organized into groups for easy reference. From basic precautions to advanced security measures, these tips cover everything you need to safeguard your devices against potential threats.

Basic Security Practices for All Devices
Basic security practices are essential for maintaining the safety of any smart device. These foundational measures address common vulnerabilities and ensure that your devices remain resilient against everyday threats. By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of becoming a victim of cyberattacks.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
Weak or reused passwords make your devices easy targets for hackers. Create passwords that combine uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using personal information like names or birthdates. - Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a text message or app-generated code. This feature is crucial for sensitive accounts like emails and financial apps. - Keep your device firmware and applications up to date.
Regular updates patch vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit. Set devices to update automatically or check for updates frequently. Outdated software is one of the most common entry points for cybercriminals. - Avoid using default passwords set by manufacturers.
Many devices ship with pre-set passwords like “admin” or “password123,” which are widely known. Change these immediately to a secure alternative upon setup. - Use a strong password for your home Wi-Fi network.
A secure Wi-Fi password prevents unauthorized users from accessing your network. Combine numbers, symbols, and random characters to create a robust password. - Turn off features like remote access when not in use.
Remote access allows you to control your device from anywhere, but it also opens a gateway for hackers. Only enable this feature when necessary and ensure it’s secured with a strong password. - Regularly review the devices connected to your network.
Use your router’s settings or a network management app to identify unknown devices. Disconnect or block any devices you don’t recognize. - Disable Bluetooth and Wi-Fi when not needed.
Leaving Bluetooth or Wi-Fi on unnecessarily increases your exposure to cyber threats. Turn these off when you’re not using them to minimize risk. - Avoid connecting to unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
Public networks are often unencrypted, allowing attackers to intercept your data. Use a trusted VPN service to encrypt your connection if you must use public Wi-Fi. - Set up a secure lock screen on smartphones and tablets.
Use PINs, passwords, or biometric options like fingerprints or facial recognition to prevent unauthorized access to your devices.

Protecting Your Home Network
Your home network serves as the backbone of your smart device ecosystem, making it a primary target for attackers. Properly securing your Wi-Fi and router settings can significantly enhance the safety of all connected devices. These tips focus on hardening your home network against intrusion.
- Change the default administrator credentials on your router.
Default credentials like “admin” and “password” are easily guessed by hackers. Set a strong, unique username and password for your router’s admin panel. - Enable WPA3 encryption for your Wi-Fi network.
WPA3 is the latest standard for Wi-Fi security, offering enhanced encryption. Check your router settings to ensure WPA3 is enabled, or upgrade your router if necessary. - Set up a guest Wi-Fi network for visitors.
Allowing guests to connect to your primary network increases the risk of exposure. Create a separate network for guests with limited access to critical devices. - Enable a firewall on your router.
Most modern routers include built-in firewalls to monitor incoming and outgoing traffic. Enable this feature to block unauthorized access attempts. - Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup).
WPS is a convenient but insecure feature that allows devices to connect via a PIN. Disabling WPS reduces the risk of brute-force attacks. - Regularly reboot your router.
Rebooting your router can disrupt malware that may have infected your network. Make it a habit to restart your router periodically. - Use a router with automatic firmware updates.
Many routers now include automatic update features to patch vulnerabilities. If your router doesn’t support this, manually check for firmware updates regularly. - Check your router’s connected devices list.
Log in to your router’s admin panel to view all connected devices. Remove any unfamiliar devices immediately. - Turn off SSID broadcasting if you don’t need it.
Hiding your network name (SSID) makes it harder for outsiders to detect and connect to your Wi-Fi. - Use a VPN for your home network.
A VPN encrypts all traffic between your devices and the internet, providing an additional layer of security.
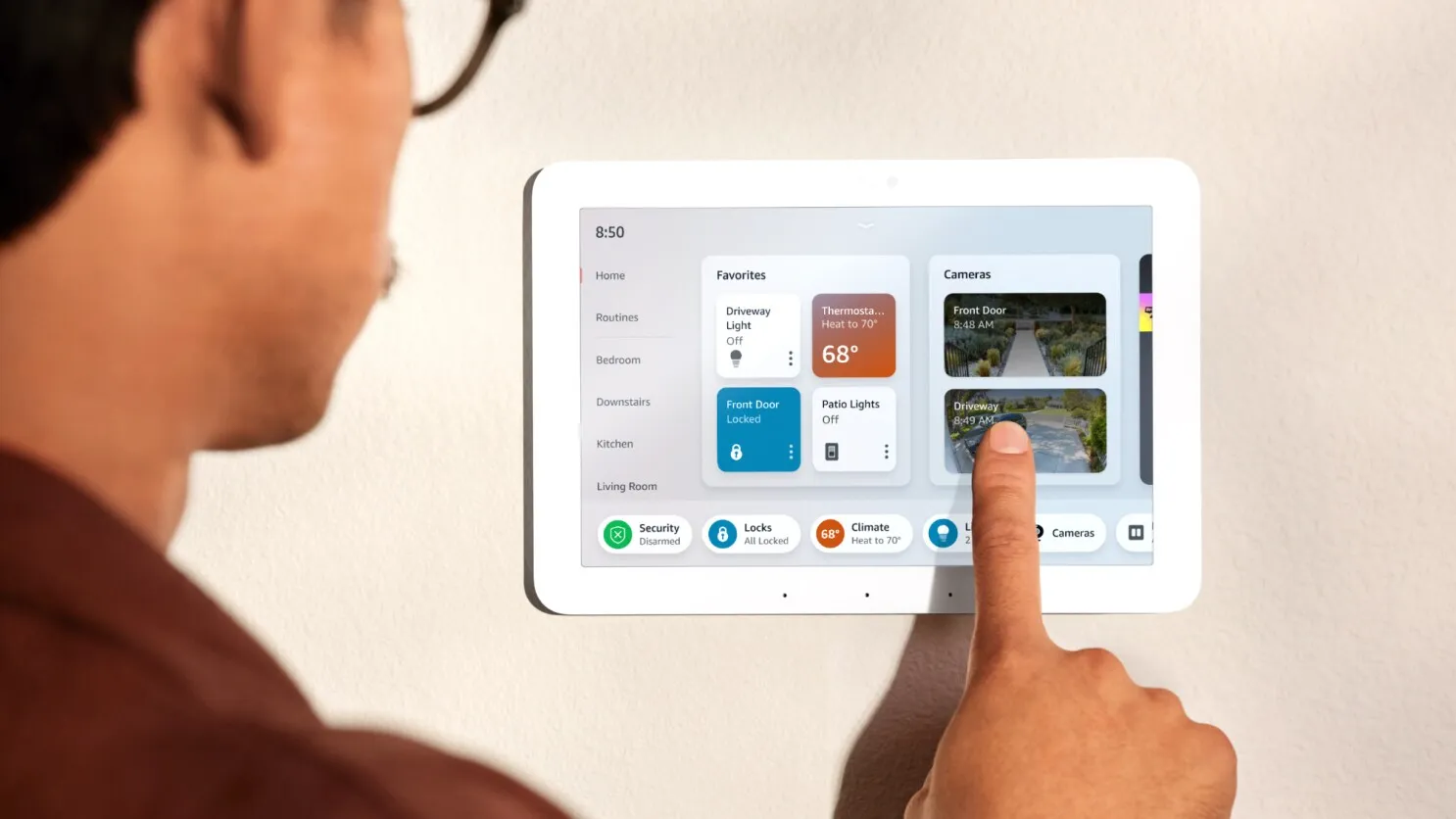
Securing Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices like thermostats, cameras, and voice assistants are increasingly popular but can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. Securing these gadgets is crucial to protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access to your home. These tips help ensure your smart home remains safe.
- Change default passwords for all smart home devices.
Manufacturers often set default passwords for smart devices, which are widely known. Update these to strong, unique passwords during setup. - Place smart home hubs on a separate network.
Use a guest network or VLAN for your smart home devices to isolate them from your primary devices like laptops and phones. - Disable unused features on smart home devices.
Features like remote access, voice activation, or geolocation may not always be necessary. Disabling them reduces potential vulnerabilities. - Monitor smart cameras for unauthorized access.
Regularly check your security cameras’ access logs and settings. Enable notifications for login attempts to detect suspicious activity. - Keep smart devices’ firmware up to date.
Many smart home devices receive periodic updates to fix security flaws. Check the manufacturer’s website or app for update notifications. - Turn off devices when not in use.
Gadgets like smart speakers and cameras can still transmit data when idle. Powering them down when unnecessary limits data exposure. - Disable microphone access for voice assistants if unused.
If you’re not actively using your voice assistant, disable its microphone to prevent accidental activation and data collection. - Use two-factor authentication for smart home accounts.
Many smart home ecosystems, such as Google Home or Alexa, support 2FA. Enable it for an added layer of security. - Review permissions for smart home apps.
Ensure the apps controlling your devices have minimal access to personal data and permissions. Remove unnecessary permissions where possible. - Monitor IoT traffic with a network scanner.
Tools like Fing or GlassWire can help you track IoT device activity on your network, alerting you to unusual behaviour.

Securing Smartphones and Tablets
Smartphones and tablets are among the most frequently used smart devices, often storing sensitive personal and financial data. Ensuring their security is crucial to protecting your information from unauthorized access, malware, and phishing attempts. These tips help you safeguard your mobile devices and their contents.
- Install apps only from official stores.
Download apps exclusively from trusted platforms like Google Play Store or Apple App Store. Avoid third-party websites, as they are more likely to host malicious applications. - Keep your device’s operating system updated.
Regular software updates include patches for known vulnerabilities. Enable automatic updates to ensure your device is always running the latest version. - Use a strong PIN or biometric lock screen.
Secure your smartphone or tablet with a PIN, password, or biometric lock (fingerprint or facial recognition) to prevent unauthorized access. - Avoid jailbreaking or rooting your device.
While these practices can give you additional control, they bypass important security features, making your device vulnerable to malware and hacking. - Enable encryption for sensitive data.
Modern smartphones often have built-in encryption to protect your data. Check your device settings to ensure this feature is activated. - Be cautious with app permissions.
Review the permissions requested by apps and only allow access to essential features. Avoid granting unnecessary access to sensitive data like contacts, location, or microphone. - Use a reputable mobile antivirus app.
Install a trusted antivirus app to scan for malicious software and protect your device from potential threats. Many apps also offer features like phishing detection. - Enable remote wipe functionality.
Set up remote wipe on your device so you can erase its contents if it’s lost or stolen. Services like Find My iPhone or Android Device Manager offer this feature. - Avoid connecting to public charging stations.
Public USB ports can be a source of malware through “juice jacking.” Use your own charger or a USB data blocker when charging in public places. - Secure your messaging apps with encryption.
Use messaging apps that offer end-to-end encryption, such as Signal or WhatsApp, to ensure your conversations remain private.

Protecting Wearable Devices
Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers are convenient but often overlooked in terms of security. These gadgets collect sensitive data, including health metrics and location information, which makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Securing your wearables is essential for maintaining privacy and safety.
- Set up a strong passcode on your wearable device.
Many smartwatches and trackers support passcodes. Use this feature to prevent unauthorized access to your data. - Regularly update the firmware of your wearable.
Manufacturers release firmware updates to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. Check the companion app or device settings for update notifications. - Disable features you don’t use.
Turn off Bluetooth, GPS, and NFC on your wearable device when they’re not needed. These features can expose your device to unnecessary risks. - Review the permissions of the companion app.
Wearable devices are typically paired with a smartphone app. Ensure the app doesn’t have excessive permissions, such as unnecessary access to your contacts or camera. - Avoid pairing your wearable with unsecured devices.
Only connect your wearable to trusted smartphones or tablets. Unsecured pairings can expose your device to hacking attempts. - Use a secure connection for syncing data.
Sync your wearable device with its app over a secure Wi-Fi network. Avoid syncing on public networks to prevent interception of your data. - Limit data sharing with third-party apps.
Many wearable apps allow you to share data with third-party services. Review these connections and disable any that aren’t essential. - Protect your wearable with antivirus software if available.
Some wearables support third-party security apps. Check if your device has this feature and install a reputable antivirus tool. - Monitor activity logs for unusual behavior.
Regularly check your wearable’s activity and usage logs for unexpected patterns, such as unauthorized connections or excessive data usage. - Unpair your wearable from old devices.
If you no longer use a device your wearable was paired with, unpair it to prevent unauthorized access to your data.

Advanced Security Practices for Tech-Savvy Users
For those who want to go beyond basic security measures, advanced practices offer enhanced protection against sophisticated threats. These tips require a bit more technical knowledge but provide robust defences for smart devices and networks.
- Set up a dedicated IoT network.
Create a separate network for your smart devices to isolate them from primary devices like computers and smartphones. This minimizes the impact of a breach. - Use a hardware firewall for your home network.
A hardware firewall adds an extra layer of protection by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. Devices like Ubiquiti or SonicWall offer excellent options. - Enable MAC address filtering on your router.
Restrict network access to specific devices by enabling MAC address filtering. This feature limits which devices can connect to your Wi-Fi. - Turn off UPnP (Universal Plug and Play).
UPnP is a convenient feature for device communication but can be exploited by hackers. Disable it in your router’s settings unless absolutely necessary. - Install security-focused DNS services.
Use DNS services like OpenDNS or Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 to block malicious websites and improve network security. - Set up an intrusion detection system (IDS).
Tools like Snort or Suricata monitor your network for suspicious activity, alerting you to potential intrusions. - Secure your network with VLANs.
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) allow you to segment your network, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to critical devices. - Enable logging on your router and devices.
Logging helps you track activity and identify unusual patterns, which can be crucial for detecting security breaches. - Use encrypted DNS (DNS over HTTPS or DNS over TLS).
Encrypting DNS requests prevents attackers from intercepting your browsing activity. Check if your router supports this feature. - Invest in a mesh Wi-Fi system with security features.
Many modern mesh systems include built-in security tools like malware blocking and advanced parental controls.

Securing Smart TVs and Entertainment Devices
Smart TVs and entertainment devices like streaming sticks and gaming consoles are increasingly connected to the internet. While they offer endless entertainment, they also pose potential security risks, such as unauthorized access or malware attacks. Securing these devices ensures a safe and uninterrupted entertainment experience.
- Update your smart TV’s firmware regularly.
Manufacturers release updates to fix bugs and vulnerabilities. Check your TV’s settings for firmware updates and enable automatic updates if available. - Disable unused features like voice recognition.
Smart TVs often include features like voice recognition or motion sensors. Disable these if you don’t use them to minimize the risk of data collection or hacking. - Avoid installing third-party apps on your smart TV.
Stick to apps available in the official app store for your device. Third-party apps can contain malware or pose other security risks. - Use a secure and private Wi-Fi network.
Connect your smart TV to a home network that is secured with a strong password and WPA3 encryption. Avoid using public or open Wi-Fi networks. - Turn off your smart TV when not in use.
Keeping your TV off when it’s not needed reduces exposure to potential attacks and minimizes unnecessary data sharing. - Enable security features provided by your TV’s manufacturer.
Many smart TVs now include built-in security tools, such as safe browsing and app scanning. Check your device settings for available options. - Disconnect the TV’s internet access when unnecessary.
If you’re only watching local content, disconnect your smart TV from the internet to eliminate network vulnerabilities. - Use a VPN with your streaming devices.
A VPN encrypts your connection, protecting your data while streaming. Many smart TVs and devices like Roku or Fire Stick support VPNs through apps or routers. - Log out of accounts when selling or recycling.
Before selling or disposing of your smart TV, ensure all personal accounts are logged out and the device is reset to factory settings. - Avoid inputting sensitive information directly on the TV.
Use a secure companion app on your phone for logging into services instead of typing passwords on your smart TV.

Securing Gaming Consoles
Gaming consoles are no longer just for gaming—they function as multimedia hubs and connect users to online services. This connectivity makes them potential targets for hackers looking to access personal data or hijack accounts. Securing your console ensures a safe gaming environment and protects sensitive information.
- Enable two-factor authentication for your gaming accounts.
Most major gaming platforms, like PlayStation Network, Xbox Live, and Steam, support 2FA. Enable this to secure your accounts against unauthorized access. - Use strong, unique passwords for gaming profiles.
Avoid reusing passwords from other accounts. Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords. - Avoid sharing account credentials with others.
Sharing accounts may be convenient but exposes your profile to potential misuse or breaches. Keep login details private. - Secure your console with parental controls.
Set up restrictions to prevent unauthorized purchases or access to age-inappropriate content. These controls also protect your financial information. - Install firmware updates for your gaming console.
Console manufacturers regularly release updates to address vulnerabilities and enhance security. Enable automatic updates where possible. - Be cautious with third-party mods or cheats.
Avoid downloading mods or cheats from unverified sources. These files can contain malware or compromise your account. - Log out of gaming accounts when using shared consoles.
If you use a shared or public console, ensure you log out of your profile to prevent unauthorized access to your account. - Use a private network for online gaming.
Avoid using public Wi-Fi for gaming, as these networks are prone to attacks. Use a secure home network or a VPN for added protection. - Review permissions for gaming apps.
Many gaming apps request access to your camera, microphone, or contacts. Limit permissions to only what is necessary for the app to function. - Monitor account activity for unusual transactions.
Regularly check your gaming accounts for unauthorized purchases or login attempts. Most platforms allow you to review transaction and login histories.

Workplace Devices and BYOD Security
In workplaces that allow Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, ensuring security for personal devices used for work is critical. Unsecured devices can lead to data breaches, jeopardizing sensitive company information. These tips focus on maintaining a secure environment for workplace devices.
- Install mobile device management (MDM) software.
Many organizations provide MDM solutions to monitor and manage workplace devices. These tools help enforce security policies and ensure compliance. - Separate work and personal data on your device.
Use separate accounts or containers for work-related apps and data. This minimizes the risk of personal activities compromising workplace security. - Enable remote wipe for workplace devices.
Ensure your device can be remotely wiped in case it’s lost or stolen. This feature is essential for protecting sensitive business data. - Use company-provided VPNs for work access.
Connect to your workplace network only through approved VPNs. This ensures that your connection is encrypted and secure. - Avoid downloading unapproved software on work devices.
Installing unauthorized apps can introduce malware or create vulnerabilities. Follow your organization’s software policies. - Secure workplace devices with strong passcodes.
Use complex passwords or biometrics to lock your device, preventing unauthorized access to corporate data. - Log out of workplace accounts after use.
Always log out of sensitive systems, especially when using shared or temporary devices for work purposes. - Keep work-related communications encrypted.
Use approved tools for communication that offer end-to-end encryption. Avoid using personal messaging apps for professional discussions. - Disable external storage access.
Many devices allow you to block access to USB drives or external storage devices. Enable this restriction to prevent unauthorized data transfer. - Regularly back up work data securely.
Use approved cloud storage or encrypted local backups for critical work data. Regular backups ensure data recovery in case of an attack.
Advanced Privacy Practices for All Devices
As technology evolves, so do the tactics used by cybercriminals to compromise privacy. Advanced privacy practices ensure that even the most sensitive data on your devices remains protected. These tips go beyond basic security, focusing on strengthening your digital privacy against sophisticated threats.
- Use privacy-focused search engines like DuckDuckGo.
Replace traditional search engines with privacy-focused alternatives that don’t track your searches or personal information. DuckDuckGo and Startpage are excellent choices. - Disable location tracking on devices.
Many apps continuously track your location. Turn off location services for apps that don’t require it, and use approximate location sharing when possible. - Install a trusted ad blocker.
Ad blockers not only prevent intrusive ads but also block trackers that monitor your browsing activity. Options like uBlock Origin or AdGuard offer robust privacy protection. - Use encrypted email services like ProtonMail.
Standard email services often lack sufficient encryption. Switch to secure providers that prioritize privacy and offer end-to-end encryption for communications. - Enable app-specific permissions for microphones and cameras.
Regularly review which apps have access to your device’s microphone and camera. Grant access only to trusted apps and disable permissions when not in use. - Use privacy screens for mobile and laptop displays.
Privacy screens reduce the viewing angle, preventing others from seeing your screen in public places. This is particularly useful for work devices. - Monitor dark web activity for data breaches.
Use services like Have I Been Pwned or your password manager to check if your data has been exposed in breaches. Change compromised passwords immediately. - Use disposable email addresses for non-critical signups.
Create temporary email accounts to avoid sharing your primary address with untrusted services. Services like TempMail can generate disposable emails. - Set up self-destructing messages on messaging apps.
Apps like Signal and Telegram offer self-destructing messages that disappear after a set time. Use this feature for sensitive conversations. - Use browser extensions to block trackers.
Extensions like Privacy Badger and Ghostery block invisible trackers that collect your browsing data without consent.

Securing your smart devices is more important than ever in today’s interconnected world. From smartphones and wearables to smart TVs and workplace devices, each gadget presents unique challenges that require tailored solutions. By implementing these 90+ tips, you can minimize risks and protect your devices, data, and privacy.
Remember, smart device security is an ongoing process. Stay vigilant by updating your devices, using strong authentication methods, and monitoring your network regularly. Taking these steps will help you enjoy the benefits of smart technology without compromising your safety. Stay secure and stay smart!










