In an extraordinary leap into what sounds like the realm of science fiction, scientists have now engineered organisms that operate in a so-called “third state” of existence, neither alive nor dead. This new classification could revolutionize our understanding of biology and open up unprecedented possibilities in medical science and beyond.
A Revolutionary Concept in Modern Science
In a recent study review published in the journal Physiology, biologists Peter Noble and Alex Pozhitkov discuss this innovative breakthrough, detailing the methods employed to create these unique entities. Originally discussed in an essay in The Conversation, the authors describe how this “third state” challenges conventional perceptions of cellular behaviour, potentially rewriting the biological rulebook.
“Organisms have long been known to change in ways that we don’t fully understand,” Noble and Pozhitkov noted, emphasizing the groundbreaking nature of their work. Unlike natural organisms that follow a predetermined evolutionary path—like caterpillars transforming into butterflies—these newly created biobots exhibit capabilities that go beyond their original design and programming.
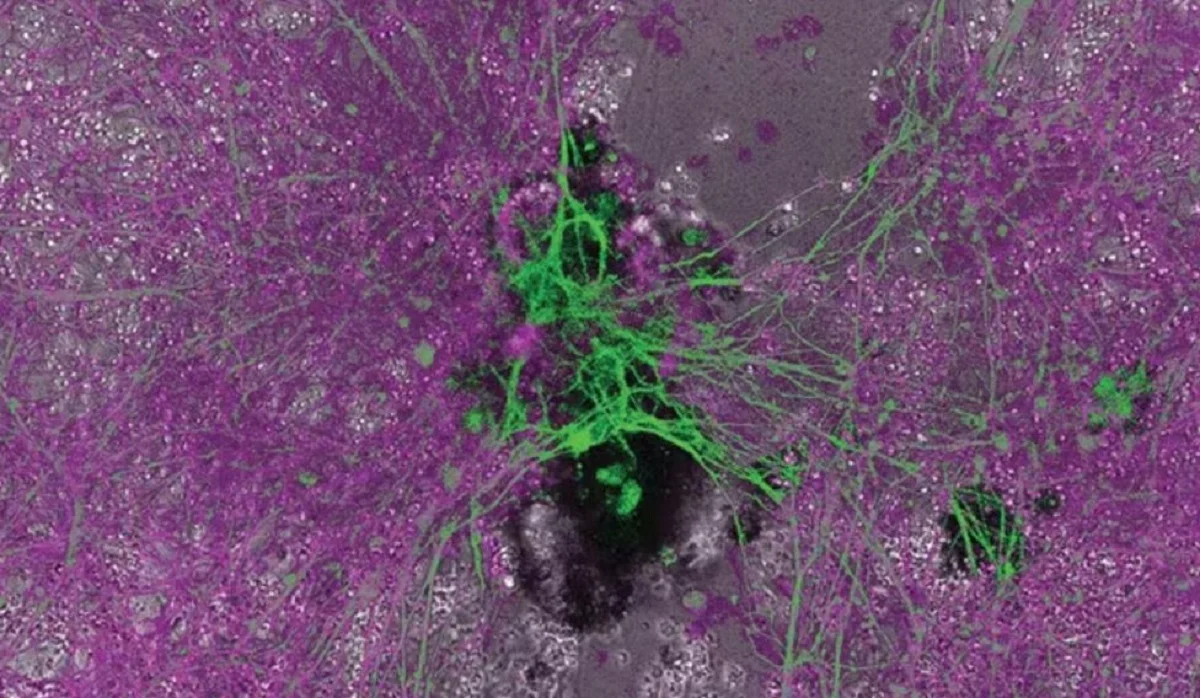
Unveiling the Potential of Biobots
The most exciting aspect of these organisms is their radical functionality. Scientists have observed these biobots performing tasks as advanced as repairing damaged neuron cells in laboratory settings. This suggests a future where synthetic organisms could be designed to carry out specific, beneficial tasks in medical applications, environmental conservation, and more.
As the researchers forge ahead, the scientific community and the world at large eagerly anticipate the next developments. These could potentially include enhancements to existing biobots and xenobots—another form of synthetic life that has been the subject of recent studies.

The Implications of Discovering a New State of Being
The creation of life forms residing in this third state holds profound implications for science and our entire understanding of life itself. It beckons questions about the essence of life and the ethical considerations of creating organisms that exist in this liminal space. As research continues, exploring these philosophical and moral questions alongside scientific advancements will be crucial.
For now, the promise of these biobots lies in their potential to perform tasks beyond current scientific expectations. They offer a glimpse into a future where the line between organic and synthetic, between life and non-life, becomes increasingly blurred. With continued research and development, the mysteries of this third state may soon yield technologies that could transform our world in ways we are only beginning to imagine.